Know the Facts About…Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
by Karen Rollins Jul 8, 2019

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition which affects how a woman’s ovaries works and impacts hormone levels.
Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones which causes them to skip menstrual periods and makes it harder for them to get pregnant.
PCOS also contributes to long term health issues such as diabetes and high cholesterol levels and can cause excess hair growth on the face and body and baldness.
What is PCOS?
The three main features of PCOS are:
– Irregular or skipped periods
– Ovarian cysts
– High levels of male hormones
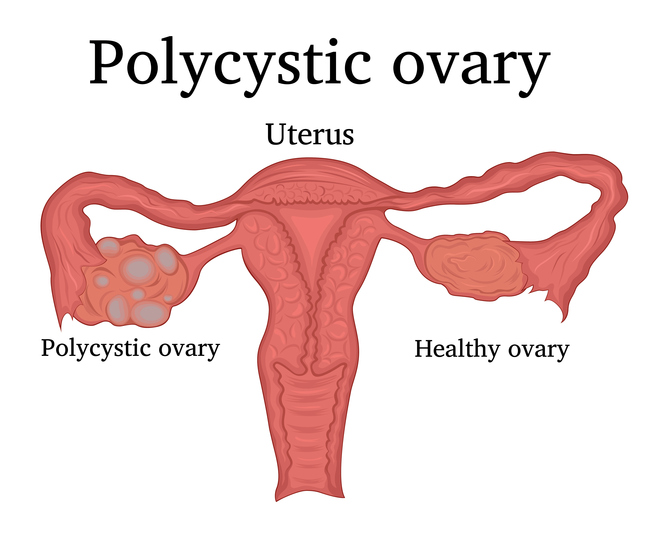
PCOS affects a woman’s ovaries, the reproductive organs that produce hormones which regulate the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce a small number of male hormones called androgens.
In PCOS, several fluid-filled sacs grow inside the ovaries. These sacs are follicles which contain an immature egg. The eggs never mature enough to trigger ovulation and this lack of ovulation alters hormone levels meaning estrogen and progesterone levels are lower than usual, while androgen levels are higher.
Extra male hormones disrupt the menstrual cycle, so women with PCOS get fewer periods than usual.
PCOS affects women during their childbearing years from age 15 to 44, but many women have the condition and don’t even know it, because they don’t have any symptoms.
What are the symptoms?
The most common PCOS symptoms are:
– Irregular or no periods: A lack of ovulation prevents the uterine lining from shedding every month as normal. Some women with PCOS get fewer than eight periods a year or none.
– Difficulty getting pregnant: Due to irregular ovulation or not ovulating at all.
– Acne: Male hormones can make the skin oilier than usual and cause breakouts.
– Excess hair growth: More than 70 per cent of women with this condition grow excess hair on their face and body.
– Weight gain: Up to 80 per cent of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
– Thinning hair: Hair on the scalp thins and falls out.
– Headaches: Hormone changes can cause headaches in some women.
What causes PCOS?
The exact cause of the condition is not known but it is believed to be hereditary and tied to abnormal hormone levels including high levels of insulin.
Can PCOS be cured?
There’s no cure for PCOS but there are ways to control the symptoms. If you think you have the condition you should speak to your GP.
Medications are available to treat symptoms such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth, and fertility problems.
With treatment, most women with PCOS can get pregnant.
Sources: NHS UK / Healthline