How to Identify if Your Cortisol Levels Are Too High or Low
by Carolyn Lee Apr 22, 2024

Cortisol is an essential glucocorticoid hormone produced and released by the adrenal glands. Hormones are chemicals that coordinate different bodily functions, carrying messages through the blood to your skin, organs, muscles, and other tissues. Your body continuously monitors your cortisol levels to maintain stable levels.
What role does cortisol play in the body?
Cortisol regulates the body’s stress response, blood pressure, and blood sugar. It controls the body’s use of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. This hormone also helps to maintain your sleep-wake cycle and suppresses inflammation. Deviations from normal cortisol levels, lower or higher than usual, can harm your overall health.
Cortisol and stress.
Your body responds to different forms of stress, including chronic, acute, and traumatic. When stressed, your body releases signals from hormones and nerves. These signals cause your adrenal glands to release hormones (cortisol and adrenaline). Although cortisol is often called the “stress hormone,” it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
Possible causes for low or high levels of cortisol.
Experiencing unusually high levels of cortisol for an extended period is generally linked to a rare condition called Cushing’s syndrome. Causes for higher-than-normal cortisol levels and Cushing’s syndrome include tumours in the pituitary gland, taking large amounts of corticosteroid medications, or adrenal gland tumours.
Lower-than-normal cortisol levels are considered adrenal insufficiency, with the two main types being primary and secondary. Primary adrenal insufficiency typically results from an autoimmune reaction where your immune system unexpectedly attacks healthy cells in your adrenal glands. Your adrenal glands can also become damaged from blood loss to the tissues or an infection. Secondary adrenal insufficiency can result from a pituitary tumour or an underactive pituitary gland.
Symptoms of high cortisol.
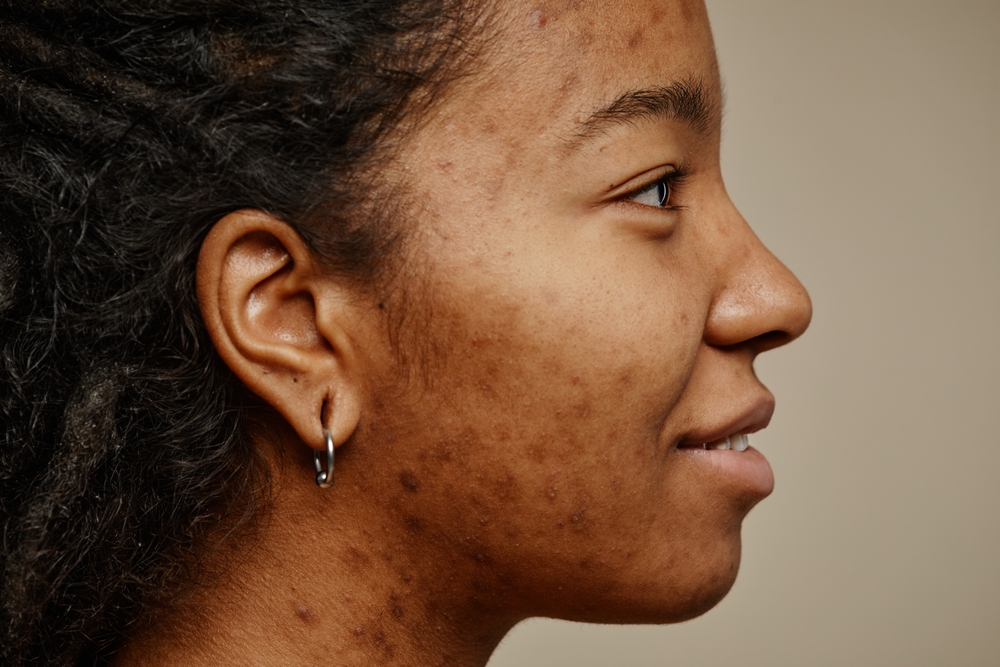
Typical signs of increased cortisol levels include muscle weakness, acne, extreme fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and high blood pressure. Thinning skin, easy bruising, slow healing, and weight gain (mainly around the abdomen and face) are also symptoms of increased cortisol levels.
Symptoms of low cortisol and possible causes.
Some symptoms of low cortisol levels in the body include low blood pressure, poor appetite, fatigue, and unintentional weight loss.
Why is managing high cortisol crucial?
Poorly managed high cortisol levels can have severe consequences on your health. If left untreated, high cortisol can increase your risk of severe health conditions, including psychiatric disorders, cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance diabetes, and osteoporosis.
When should you see a doctor?
High cortisol levels can cause several symptoms. However, many of these symptoms are not specific to increased cortisol levels. You should visit a doctor for a formal diagnosis. Your doctor might suggest that you do a blood, saliva, or urine test to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. They will help you treat or manage the condition.
Please use Find Yello to search for doctors, medical specialists, and related services that can help you.
Sources: Healthline, Cleveland Clinic, Health Direct, and WebMD.